

Thinking about filing for bankruptcy in Germany? Understanding the bankruptcy procedure is crucial for a smooth process. Whether you’re an individual or a business owner, this article will guide you through the steps involved in filing for bankruptcy in Germany.
In Germany, bankruptcy proceedings are governed by the Insolvency Code. The procedure begins with filing an insolvency petition at the local district court. From there, a court-appointed insolvency administrator will take charge of your assets and liabilities, establishing a clear picture of your financial situation.
The key objective of bankruptcy proceedings in Germany is to provide fair treatment to creditors while giving debtors a chance to recover financially. During this process, your assets may be liquidated to repay your debts, but exemptions may apply based on your specific circumstances.
Staying knowledgeable about the bankruptcy procedure in Germany can help you navigate the process more effectively. Whether you’re looking for ways to rebuild your finances or considering alternative debt relief options, understanding the bankruptcy process is essential. Read on to learn more about the bankruptcy procedure in Germany and explore the available avenues for managing your debt.
Bankruptcy in Germany can be classified into two main types: personal bankruptcy and business bankruptcy. Personal bankruptcy, also known as consumer bankruptcy, applies to individuals who are unable to meet their financial obligations. Business bankruptcy, on the other hand, pertains to companies that are facing financial insolvency.
Personal bankruptcy in Germany is designed to provide individuals with a fresh start by eliminating their debts. To file for personal bankruptcy, you must be insolvent and unable to pay your debts as they become due. Insolvency can be caused by various factors such as unemployment, illness, or excessive debt burdens.
When filing for personal bankruptcy in Germany, you must provide detailed information about your assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. This information is crucial for the court-appointed insolvency administrator to assess your financial situation and determine the best course of action. During the bankruptcy process, your assets may be liquidated to repay your debts, but certain exemptions exist to protect essential items such as your home and personal belongings.
Business bankruptcy in Germany applies to companies that are unable to meet their financial obligations. This can be due to factors such as declining sales, excessive debt, or mismanagement. Filing for business bankruptcy allows the company to restructure its debts, liquidate assets, or seek a buyer to continue operations.
To file for business bankruptcy in Germany, the company must be insolvent and unable to pay its debts as they become due. The court-appointed insolvency administrator will assess the company’s financial situation and work towards a solution that benefits both creditors and the company. This could involve liquidating assets to repay debts or implementing a debt repayment plan.
To be eligible for bankruptcy in Germany, certain requirements must be met. For personal bankruptcy, you must be insolvent and unable to pay your debts. It’s important to note that the insolvency threshold varies depending on your personal circumstances. For example, if you’re a single individual, your insolvency threshold will differ from that of a family with dependents.
For business bankruptcy, the company must also be insolvent and unable to meet its financial obligations. The insolvency threshold for businesses is determined by factors such as the company’s assets, liabilities, and ability to generate revenue. It’s advisable to consult with a legal professional to assess your eligibility for bankruptcy based on your specific situation.
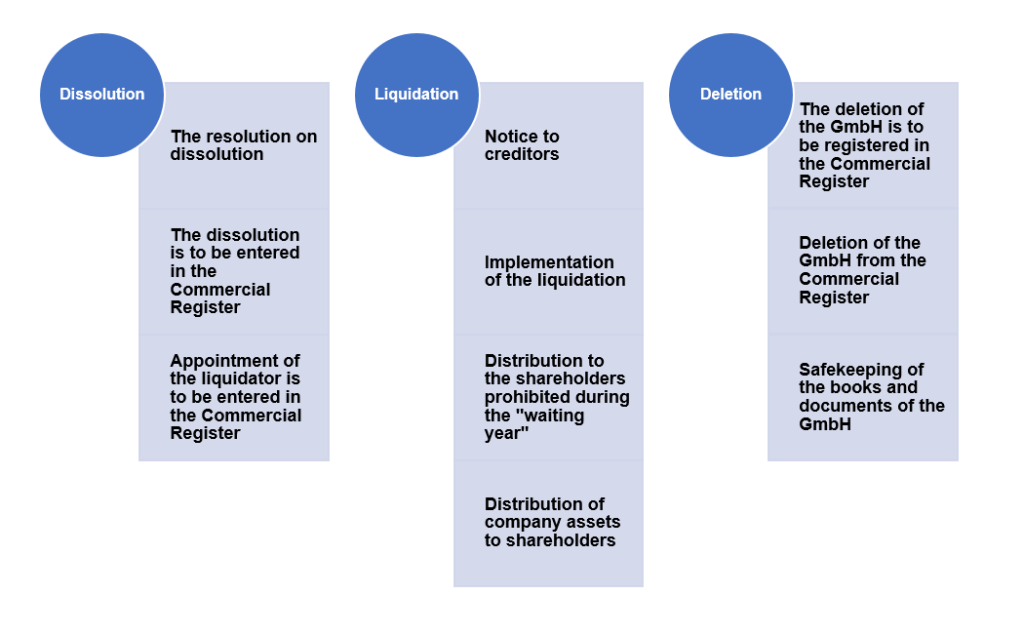
Filing for bankruptcy in Germany involves several key steps. Understanding these steps can help you navigate the process more effectively and ensure a smoother transition towards financial recovery.
The first step in the bankruptcy process is filing an insolvency petition at the local district court. This petition should include detailed information about your financial situation, including your assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. It’s crucial to provide accurate and complete information to avoid delays or complications in the process.
Once the insolvency petition is filed, the court will appoint an insolvency administrator to oversee the bankruptcy proceedings. The insolvency administrator is a qualified professional who acts as an independent party to manage your assets and liabilities. They will assess your financial situation, verify the information provided, and ensure fair treatment for both creditors and debtors.
During the bankruptcy process, creditors will have the opportunity to submit their claims to the insolvency administrator. These claims will be verified and assessed based on their legitimacy. The insolvency administrator will work towards distributing the available assets fairly among the creditors.
In some cases, the liquidation of assets may be necessary to repay the debts. The insolvency administrator will identify and value your assets, including properties, vehicles, and other belongings. These assets may be sold to generate funds for debt repayment. However, it’s important to note that exemptions exist to protect essential items such as your primary residence and necessary household goods.
Bankruptcy proceedings in Germany aim to provide debtors with an opportunity to recover financially. Depending on your circumstances, the insolvency administrator may propose a debt repayment plan or restructuring option. This could involve negotiating with creditors to reduce the debt amount, extend the repayment period, or establish a new repayment schedule. These plans or options are designed to help debtors regain control of their finances and work towards a fresh start.
Once the bankruptcy process is completed, you may be eligible for a discharge of your debts. This means that your remaining debts will be legally eliminated, providing you with a fresh financial start. The discharge of debts is subject to certain conditions, and it’s important to consult with a legal professional to understand the implications and requirements.
Throughout the bankruptcy process in Germany, the bankruptcy court and the appointed insolvency administrator play crucial roles in ensuring fair treatment for both debtors and creditors. The bankruptcy court oversees the proceedings, reviews the insolvency petition, and appoints the insolvency administrator. Their primary objective is to facilitate a transparent and efficient bankruptcy process.
The insolvency administrator, on the other hand, acts as an independent party to manage your assets and liabilities. They assess your financial situation, verify claims, and distribute available assets among the creditors. Their role is to ensure fair treatment for all parties involved and work towards a solution that maximizes the recovery for creditors while giving debtors a chance to recover financially.
In bankruptcy proceedings, the liquidation of assets may be necessary to repay the debts owed to creditors. The insolvency administrator will identify and value your assets, which may include properties, vehicles, investments, and other belongings. These assets will be liquidated and converted into cash, which will then be distributed among the creditors according to their claims.
However, it’s important to note that certain exemptions exist to protect essential items and ensure debtors have the means to rebuild their lives. These exemptions vary depending on your personal circumstances and may include your primary residence, necessary household goods, and tools of your trade. It’s advisable to consult with a legal professional to understand the exemptions applicable to your situation.
Bankruptcy proceedings in Germany aim to provide debtors with an opportunity to recover financially. Depending on your circumstances, the insolvency administrator may propose a debt repayment plan or restructuring option. These options are designed to help debtors regain control of their finances and work towards a fresh start.
A debt repayment plan involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the debt amount, extend the repayment period, or establish a new repayment schedule. This allows debtors to repay their debts in a manageable way while still meeting their essential living expenses. A restructuring option, on the other hand, may involve reorganizing the business’s operations, renegotiating contracts, or seeking additional funding to continue business operations.
The specific debt repayment plans and restructuring options available will depend on your financial situation and the agreement reached between you and your creditors. It’s important to work closely with the insolvency administrator and consult with a legal professional to explore the best options for your circumstances.
Bankruptcy has both immediate and long-term consequences for individuals and businesses in Germany. Understanding these consequences can help you make informed decisions and plan for the future.
Filing for personal bankruptcy in Germany may result in the following consequences:
Loss Of Assets: Depending on your financial situation, some of your assets may be liquidated to repay your debts. However, exemptions exist to protect essential items such as your primary residence and necessary household goods.
Credit Score Impact: Bankruptcy will have a negative impact on your credit score, making it difficult to obtain credit in the future. This can affect your ability to secure loans, mortgages, or even rent a property.
Limited Financial Options: After filing for bankruptcy, your financial options may be limited. It may be challenging to open new bank accounts or obtain credit cards. However, over time, as you rebuild your finances, these options may become more accessible.
Employment Implications: Bankruptcy may have implications for certain professions or industries. Some employers may consider bankruptcy as a risk factor during the hiring process. However, it’s important to note that not all employers view bankruptcy negatively, and your skills and qualifications will also be taken into consideration.
Filing for business bankruptcy in Germany may result in the following consequences:
Closure Of Business: Depending on the severity of the financial situation, business bankruptcy may result in the closure of the company. This can have significant implications for employees, suppliers, and other stakeholders.
Loss Of Assets: Assets owned by the business may be liquidated to repay the debts owed to creditors. This can include properties, equipment, inventory, and other belongings.
Credit Score Impact: Similar to personal bankruptcy, business bankruptcy will have a negative impact on the credit score of the company. This can make it challenging to obtain credit or secure funding in the future.
Reputation And Market Perception: Business bankruptcy can impact the reputation and market perception of the company. Customers and suppliers may have concerns about the company’s financial stability, which can affect relationships and future business opportunities.
Bankruptcy is not the only option for individuals and businesses facing financial difficulties in Germany. Depending on your circumstances, there may be alternative debt relief options available. These alternatives can provide a less severe impact on your financial situation while still offering a chance to regain control of your finances. Here are a few alternatives to consider:
Debt Counseling: Debt counseling services can help you assess your financial situation, develop a budget, and negotiate with creditors to establish a repayment plan. These services can provide valuable guidance and support in managing your debts.
Debt Consolidation: Debt consolidation involves combining multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate. This can make it easier to manage your debts and reduce your overall monthly payments.
Debt Settlement: Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to settle your debts for less than the full amount owed. This can provide a more manageable way to repay your debts while reducing the overall financial burden.
Informal Agreements: In some cases, informal agreements can be reached with creditors to establish a repayment plan or temporarily suspend payments. These agreements can provide temporary relief while you work towards a long-term solution.
It’s important to consult with a legal professional or financial advisor to explore the best debt relief options for your specific situation. They can assess your financial circumstances, provide guidance on the available alternatives, and help you make informed decisions.
Understanding the bankruptcy procedure in Germany is essential for individuals and businesses facing financial difficulties. Whether you’re considering filing for bankruptcy or exploring alternative debt relief options, staying informed about the process can help you navigate the challenges more effectively.
This article provided an overview of the bankruptcy procedure in Germany, including the types of bankruptcy, eligibility requirements, steps involved in the process, role of the bankruptcy court and trustee, liquidation of assets, debt repayment plans and restructuring options, consequences of bankruptcy, and alternatives to consider.
If you’re considering bankruptcy or need further information, it’s advisable to consult with a legal professional or financial advisor who specializes in insolvency matters. They can provide personalized advice based on your unique circumstances and help you make informed decisions to overcome your financial challenges.
Remember, bankruptcy is not the end of the road. With the right support and a strategic approach, you can rebuild your finances and work towards a fresh start.
Stay updated with the latest news and exclusive offers. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights delivered to your inbox!