

Are you considering entering into a business agreement in Germany? Confidentiality is an important aspect to consider in any business deal to protect your valuable information. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the confidentiality clause in Germany, ensuring you are well-informed and prepared.
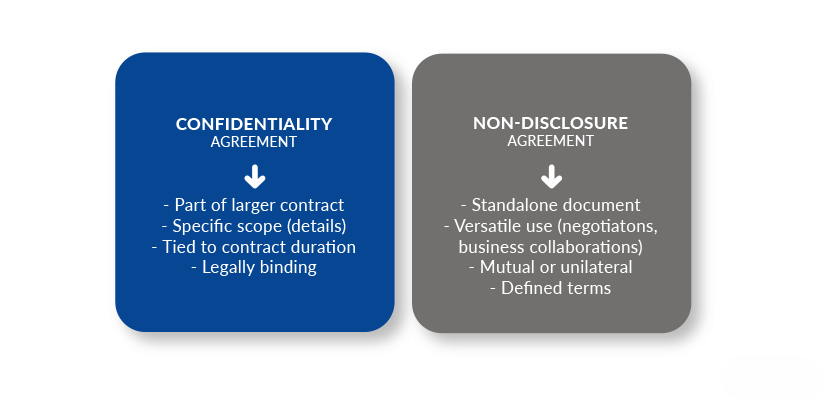
In Germany, a confidentiality clause, also known as a non-disclosure agreement, is a legally binding contract that establishes the terms and conditions for the protection of sensitive information. It specifies what information is regarded as confidential, the obligations of the parties involved, and the duration of the agreement.
Adhering to the highest standards of accuracy, this article navigates the complexities of confidentiality clauses in Germany, highlighting key considerations such as employee obligations, third-party involvement, and potential consequences of a breach. Whether you are a multinational corporation or a small business, understanding the legal framework surrounding confidentiality in Germany is essential to safeguard your interests.
Stay ahead of the game and make informed decisions by diving into the intricacies of German confidentiality clauses. Protect your intellectual property and trade secrets with confidence – read on to unravel the nuances of this vital aspect of German business law.
Confidentiality clauses serve a crucial purpose in business transactions by safeguarding sensitive information. In Germany, these clauses are essential for protecting trade secrets, proprietary information, and other valuable assets. By including a confidentiality clause in your business agreements, you ensure that the information shared remains confidential and cannot be disclosed to third parties without proper authorization.
A well-crafted confidentiality clause sets clear expectations and obligations for all parties involved. It establishes the scope of what constitutes confidential information, outlines the duties of secrecy placed upon the individuals privy to the information, and defines the consequences of a breach. This level of clarity helps to prevent misunderstandings and disputes, fostering trust and confidence among the parties.
In Germany, the legal framework for confidentiality clauses is primarily governed by the Civil Code (Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch or BGB). The BGB provides the foundation for contractual agreements, including confidentiality clauses, and sets forth the general principles and regulations that apply.
Under German law, confidentiality clauses are considered valid and enforceable, as long as they meet certain requirements. The clauses must be clear, specific, and not overly broad, ensuring that the obligations imposed are reasonable and proportionate to the nature of the information being protected. Additionally, the duration of the confidentiality agreement must be reasonable and should not unduly restrict the disclosing party’s business activities.
A well-drafted confidentiality clause in Germany should contain several key elements to ensure its effectiveness and enforceability. These elements include:
Definition Of Confidential Information: The clause should clearly define the types of information that will be considered confidential. This can include trade secrets, customer data, financial information, technical know-how, and any other proprietary or sensitive information relevant to the business agreement.
Obligations Of The Parties: The confidentiality clause should outline the obligations of both the disclosing party and the receiving party. The disclosing party is responsible for providing the confidential information and expects the receiving party to handle it with utmost care and confidentiality. The receiving party, on the other hand, agrees to maintain the secrecy of the information and not disclose it to any unauthorized individuals or entities.
Duration Of The Agreement: The confidentiality clause should specify the duration for which the agreement remains in effect. This duration should be reasonable and commensurate with the nature of the information being protected. It is important to strike a balance between providing adequate protection and allowing the receiving party to carry out their business activities.
Confidentiality clauses in Germany are generally enforceable, but certain conditions must be met for effective enforcement. To ensure the enforceability of a confidentiality clause, the following factors should be considered:
Specificity And Clarity: The clause should be clear and specific in defining what constitutes confidential information and the obligations of the parties. Ambiguity or vagueness may lead to challenges in enforcement.
Proportional Obligations: The obligations imposed on the receiving party should be reasonable and proportionate to the nature of the information being protected. Courts may refuse to enforce a confidentiality clause if the obligations are deemed excessive or overly burdensome.
Consideration: The confidentiality clause should be supported by valid consideration, such as the exchange of valuable goods or services between the parties. Without consideration, the clause may be deemed unenforceable.
While confidentiality clauses provide robust protection for sensitive information, there are certain exceptions where disclosure may be permitted or required. These exceptions include:
Consent: If the disclosing party provides consent for the receiving party to disclose the information to specific individuals or entities, the confidentiality obligation may be waived.
Legal Obligations: In certain circumstances, the receiving party may be legally obligated to disclose the confidential information. This can include compliance with court orders, subpoenas, or other legal requirements.
Prior Knowledge: If the receiving party already possessed the confidential information prior to entering into the confidentiality agreement, they may not be bound by the obligations of the clause.
Drafting an effective confidentiality clause requires careful consideration of the specific circumstances and needs of the parties involved. While it is advisable to seek legal advice when drafting such clauses, the following best practices can help ensure the clause is well-crafted:
Clear And Concise Language: Use clear and concise language to define the scope of the confidential information and the obligations of the parties. Avoid using overly technical or ambiguous terms that may lead to misinterpretation.
Tailor The Clause To The Specific Agreement: Customize the confidentiality clause to suit the unique circumstances and requirements of the business agreement. Consider the nature of the information being protected, the parties involved, and the duration of the agreement.
Include Dispute Resolution Provisions: It is prudent to include provisions for dispute resolution, such as arbitration or mediation, in case of any disagreements or breaches of the confidentiality clause. This helps to resolve disputes efficiently and avoid costly litigation.
To ensure the effectiveness and enforceability of confidentiality clauses in Germany, it is important to follow some best practices during implementation and enforcement:
Educate Employees: Provide comprehensive training and education to employees who may have access to confidential information. Make them aware of their obligations and the consequences of breaching the confidentiality clause.
Monitor Compliance: Regularly monitor and assess compliance with the confidentiality clause. Implement appropriate measures, such as access controls and non-disclosure agreements with employees, to minimize the risk of unauthorized disclosures.
Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of the confidential information shared and the parties involved. This documentation can be invaluable in case of a breach and can help establish the extent of the damage suffered.
To gain a deeper understanding of the complexities and potential challenges surrounding confidentiality clauses in Germany, it is helpful to examine real-life case studies. The following examples highlight some notable confidentiality clause disputes and their outcomes:
Case Study 1: In a high-profile dispute between two tech companies, Company A accused Company B of breaching the confidentiality clause by sharing sensitive trade secrets with a competitor. The court found in favor of Company A, ruling that Company B had indeed breached the agreement and awarded significant damages.
Case Study 2: In another case, an employee of a pharmaceutical company violated the confidentiality clause by disclosing confidential research findings to a rival company. The court held the employee personally liable for the breach and ordered them to pay substantial compensation to the employer.
These case studies illustrate the potential consequences of breaching a confidentiality clause in Germany and emphasize the importance of careful drafting and enforcement.
Confidentiality clauses are an indispensable tool for protecting sensitive information in business transactions in Germany. By understanding the legal framework, key elements, and best practices surrounding confidentiality clauses, you can effectively safeguard your intellectual property and trade secrets.
Remember to tailor your confidentiality clauses to suit the specific circumstances of each agreement, educate employees on their obligations, and regularly monitor compliance. By doing so, you can minimize the risk of breaches and protect your valuable information with confidence.
Stay updated with the latest news and exclusive offers. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights delivered to your inbox!