

German agriculture has long been admired for its ability to find a delicate balance between productivity and environmental conservation. With keywords such as “German agriculture,” “productivity,” and “environmental conservation” in mind, it is evident that Germany has implemented innovative strategies to ensure the sustainability of its agricultural practices.
The success of German agriculture in striking this balance can be attributed to a combination of factors. Firstly, stringent environmental regulations and government support have played a crucial role in guiding farmers towards sustainable practices. The emphasis on resource-efficient production techniques and the use of environmentally friendly technologies has allowed German farmers to achieve high yields while minimizing the impact on the ecosystem.
Secondly, German farmers have embraced advanced precision farming techniques, leveraging technology and data to optimize crop yields, minimize chemical inputs, and reduce water consumption. By utilizing precision agriculture tools, such as satellite imaging and digital mapping, farmers can target specific areas of their fields, optimizing the use of resources and minimizing waste.
Lastly, a strong focus on research and development, coupled with effective knowledge transfer systems, enables German farmers to stay up-to-date with the latest innovations and best practices. This continuous exchange of information has facilitated the adoption of sustainable farming methods, ensuring that productivity is not compromised at the expense of the environment.
Overall, the German agricultural sector serves as a model for other nations, demonstrating that productivity and environmental conservation can go hand in hand.
Balancing productivity and environmental conservation in agriculture is no easy task. Farmers face numerous challenges in their quest to optimize yields while minimizing the impact on the environment. One of the primary challenges is the increasing global demand for food, which puts pressure on farmers to maximize production. At the same time, there is growing awareness of the environmental consequences of conventional farming practices, such as excessive pesticide use and soil degradation.
To address these challenges, German agriculture has taken a proactive approach by implementing stringent environmental regulations and policies. These regulations ensure that farmers adhere to sustainable farming practices, minimizing the use of harmful chemicals and promoting resource-efficient production techniques. Additionally, government support programs provide incentives for farmers to adopt environmentally friendly technologies and practices.
Over the years, German agricultural practices have evolved significantly to strike a balance between productivity and environmental conservation. Traditional farming methods, which relied heavily on chemical inputs and large-scale monocultures, have been gradually replaced by more sustainable approaches. This shift has been driven by changing consumer preferences, increasing environmental concerns, and advancements in technology.
One notable change in German agriculture is the adoption of precision farming techniques. Precision farming leverages technology, such as satellite imaging and digital mapping, to analyze and manage variability within fields. By understanding the unique characteristics of different areas of their fields, farmers can optimize the use of resources, reduce waste, and minimize the environmental impact. This targeted approach allows for more efficient use of fertilizers, pesticides, and water, resulting in higher yields while reducing inputs.
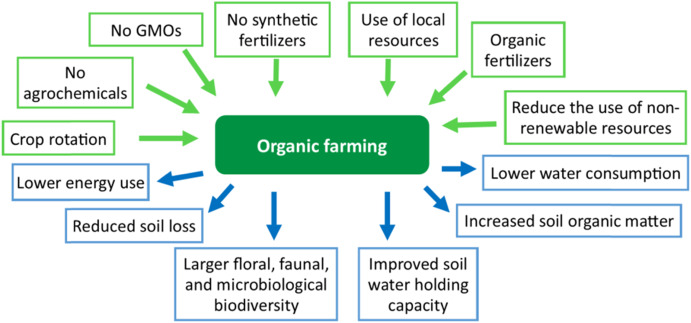
Furthermore, German farmers have embraced organic farming methods, which prioritize the use of natural fertilizers and pest control methods. Organic farming not only minimizes the use of synthetic chemicals but also promotes biodiversity and soil health. Through organic farming, German farmers have been able to meet the growing demand for organic products while contributing to the conservation of the environment.
German agriculture’s success in balancing productivity and environmental conservation is largely attributed to the stringent environmental regulations and policies implemented by the government. These regulations aim to guide farmers towards sustainable practices and minimize the negative impact of agriculture on the environment.
One key regulation is the “Greening” policy, which requires farmers to allocate a portion of their land for ecological purposes. This encourages the diversification of agricultural landscapes, promotes biodiversity, and reduces the reliance on chemical inputs. Additionally, farmers are required to implement crop rotation, which helps improve soil fertility and reduce the risk of pests and diseases.
Furthermore, the government provides financial incentives and support programs to encourage farmers to adopt sustainable farming practices. These programs offer funding for investments in environmentally friendly technologies, such as precision farming equipment and renewable energy systems. The government also provides advisory services and training to help farmers implement sustainable practices effectively.
The combination of strict regulations and government support has created a favorable environment for farmers to transition towards sustainable agriculture. This proactive approach sets a strong foundation for balancing productivity and environmental conservation in German agriculture.
Technological advancements have played a significant role in enabling German agriculture to strike a balance between productivity and environmental conservation. The adoption of advanced technologies has allowed farmers to optimize their operations, reduce inputs, and improve overall efficiency.
One key technology that has revolutionized German agriculture is precision farming. Through the use of satellite imaging, GPS, and sensors, farmers can gather precise data about their fields, such as soil composition, moisture levels, and crop health. This data enables farmers to make informed decisions regarding the application of fertilizers, pesticides, and water, resulting in more targeted and efficient resource management.
Another technological advancement is the use of drones in agriculture. Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can monitor crop health, identify pests and diseases, and even spray targeted areas with pesticides. This targeted approach minimizes the use of chemicals and reduces the environmental impact. Drones also provide valuable data for farmers, helping them identify areas of their fields that require attention and optimize their farming practices.
The use of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and biogas plants, has gained popularity in German agriculture. These systems not only reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also provide farmers with a reliable and sustainable source of energy. By embracing renewable energy, farmers can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and contribute to a greener agricultural sector.
The continuous integration of technology into German agriculture has paved the way for more sustainable practices and improved productivity. These advancements demonstrate that technological innovation and environmental conservation can go hand in hand.
Collaboration between farmers and environmental organizations has been instrumental in promoting sustainable agriculture and striking a balance between productivity and environmental conservation in Germany. By working together, farmers and environmental organizations can leverage each other’s expertise and resources to develop innovative solutions and best practices.
Environmental organizations play a vital role in raising awareness about the environmental consequences of conventional farming practices and advocating for sustainable alternatives. They provide farmers with access to research, knowledge, and training on sustainable farming methods. Environmental organizations also facilitate knowledge exchange and networking among farmers, enabling them to learn from each other’s experiences and successes.
On the other hand, farmers contribute their practical knowledge and on-the-ground experience to the collaboration. They provide valuable insights into the feasibility and practicality of implementing sustainable farming practices. Farmers also serve as ambassadors for sustainable agriculture, showcasing the benefits and successes of their practices to the wider community.
This collaboration between farmers and environmental organizations creates a synergistic relationship, where both parties work towards the common goal of sustainable agriculture. Through joint efforts, they can overcome challenges, share resources, and drive positive change in the agricultural sector.
German agriculture has adopted a range of sustainable farming techniques and practices to strike a balance between productivity and environmental conservation. These techniques prioritize resource efficiency, biodiversity, and soil health, while minimizing the use of synthetic chemicals and reducing waste.
One prominent sustainable farming technique is integrated pest management (IPM). IPM focuses on the prevention and control of pests through a combination of biological, cultural, and chemical methods. By utilizing natural predators, crop rotation, and targeted pesticide applications, farmers can effectively manage pests while minimizing the environmental impact.
Another sustainable practice is the use of cover crops. Cover crops are planted between cash crops to protect the soil, prevent erosion, and improve soil fertility. They also help reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers by fixing nitrogen in the soil naturally. Cover crops contribute to the overall health and resilience of the agricultural ecosystem.
German farmers have adopted agroforestry practices, which involve integrating trees and crops on the same land. Agroforestry systems provide multiple benefits, such as improved soil quality, enhanced biodiversity, and increased carbon sequestration. These systems promote a more sustainable and resilient agricultural landscape.
Efficient water management techniques, such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, are widely employed in German agriculture. These techniques help conserve water resources and minimize waste, while ensuring that crops receive adequate moisture for optimal growth.
The success of these sustainable farming techniques and practices in Germany serves as a testament to their effectiveness. By implementing these strategies, farmers can achieve high yields while preserving the environment for future generations.
German agriculture is home to numerous success stories of farmers who have successfully balanced productivity and environmental conservation. These farmers serve as role models for sustainable agriculture and inspire others to adopt similar practices.
One such success story is the farm of Klaus and Anna Müller, located in the Bavarian region of Germany. The Müller family has embraced organic farming methods, focusing on biodiversity and soil health. Through the use of cover crops, crop rotation, and natural pest control methods, they have been able to maintain high yields while minimizing the use of synthetic chemicals. The Müller farm is a prime example of how organic farming can be profitable, environmentally friendly, and socially responsible.
Another success story is the dairy farm of Friedrich Schmidt. Schmidt has implemented a range of sustainable practices, such as the use of renewable energy, precision feeding, and manure management. By utilizing solar panels and biogas plants, he has significantly reduced the carbon footprint of his farm. Schmidt’s commitment to sustainable agriculture has not only improved his farm’s profitability but also contributed to the overall sustainability of the dairy industry.
These success stories highlight the potential of sustainable agriculture and demonstrate that farmers can achieve economic success while protecting the environment. By sharing their experiences and outcomes, these farmers inspire others to adopt sustainable practices and contribute to a more sustainable agricultural sector.
German agriculture offers valuable lessons that other countries can learn from in their efforts to balance productivity and environmental conservation. These lessons can guide policymakers, farmers, and stakeholders towards the adoption of sustainable farming practices.
One key lesson is the importance of strict environmental regulations and government support. By implementing stringent regulations and providing financial incentives, governments can create a conducive environment for farmers to transition towards sustainable agriculture. These policies can help overcome barriers and provide the necessary resources and support for farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
Another lesson is the significance of research and development in driving innovation and knowledge transfer. Investing in agricultural research and development allows farmers to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements and best practices. Knowledge transfer systems, such as farmer networks and advisory services, facilitate the exchange of information and promote the adoption of sustainable farming techniques.
Collaboration between farmers and environmental organizations is crucial for the success of sustainable agriculture. By working together, farmers and organizations can pool their resources, share knowledge, and drive positive change in the agricultural sector. This collaboration fosters a sense of community and collective responsibility towards the environment.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced technologies, such as precision farming and renewable energy systems, can significantly contribute to the sustainability of agriculture. By embracing technology, farmers can optimize their operations, reduce inputs, and improve overall efficiency.
Overall, the lessons learned from German agriculture can serve as a blueprint for other countries seeking to strike a balance between productivity and environmental conservation. By adopting similar approaches and practices, countries can ensure the long-term sustainability of their agricultural sectors.
The success of German agriculture in striking a balance between productivity and environmental conservation sets a promising path for the future of sustainable agriculture. With stringent environmental regulations, technological advancements, and collaboration between stakeholders, Germany has demonstrated that productivity and environmental conservation can go hand in hand.
The future of sustainable agriculture lies in the continuous integration of innovative technologies, research-driven practices, and effective knowledge transfer systems. By embracing precision farming techniques, renewable energy systems, and sustainable farming practices, farmers can optimize their operations, reduce environmental impact, and improve overall productivity.
The adoption of sustainable agriculture practices should not be limited to Germany alone. Other countries can learn from Germany’s experiences and successes, adapting their approaches to suit their unique agricultural landscapes and challenges. By implementing similar strategies, countries can contribute to a more sustainable global agricultural sector.
German agriculture serves as a role model for other nations, demonstrating that it is possible to strike a balance between productivity and environmental conservation. Through a combination of stringent regulations, technological advancements, collaboration, and sustainable farming practices, German farmers have achieved high yields while preserving the environment. The future of sustainable agriculture lies in the adoption of similar approaches and practices worldwide, ensuring a prosperous and sustainable future for agriculture and the planet as a whole.
Stay updated with the latest news and exclusive offers. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights delivered to your inbox!