

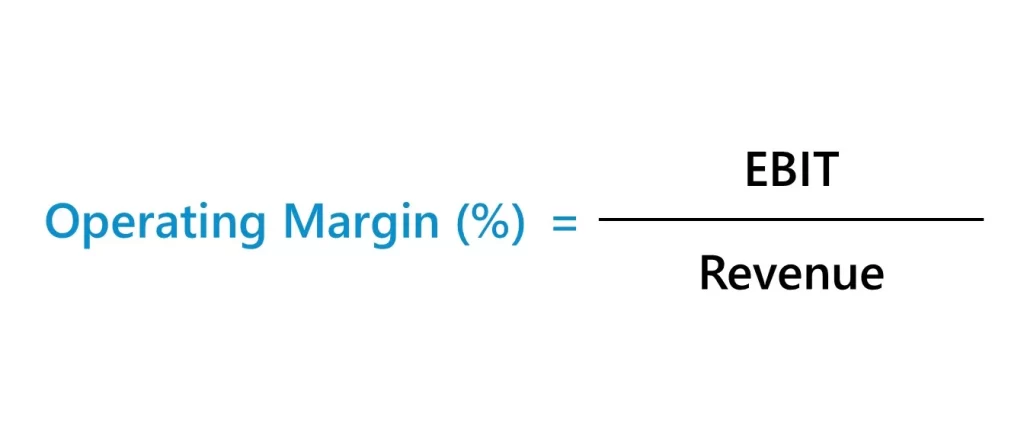
The EBIT margin is a financial metric that measures a company’s ability to generate profits from its core operations before accounting for interest and tax expenses. It is often used by investors and analysts to assess a company’s operational efficiency and profitability. By understanding the concept of EBIT, we can better grasp the factors that contribute to its calculation and how they influence a company’s profitability.
EBIT, also known as operating profit, is calculated by subtracting all operating expenses from a company’s gross profit. This includes expenses such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing costs, and other expenses directly related to the company’s core operations. EBIT does not take into account interest and tax expenses, as these can vary significantly from company to company due to factors such as debt levels and tax jurisdictions.
The EBIT margin is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing EBIT by the company’s revenue. It indicates the percentage of revenue that is generated as operating profit. A higher EBIT margin signifies that the company is able to generate a larger profit from its core operations, which is generally seen as a positive indicator of financial health and profitability.
The EBIT margin is an essential tool for assessing a company’s profitability for several reasons. Firstly, it provides a clear picture of the company’s ability to generate profits from its core operations, without being influenced by external factors such as interest and tax expenses. This allows investors and analysts to focus solely on the company’s operational efficiency.
Secondly, the EBIT margin enables meaningful comparisons between companies operating in different industries or with varying debt levels. By excluding interest expenses, which can vary significantly depending on a company’s capital structure, the EBIT margin provides a more accurate comparison of operating profitability.
Lastly, the EBIT margin helps identify trends in a company’s financial performance over time. By monitoring changes in the EBIT margin, investors and analysts can gain insights into the company’s ability to control costs, increase efficiency, and improve profitability. This information can be vital when making investment decisions or assessing the financial health of a company.
Several factors influence the calculation of the EBIT margin and can have a significant impact on a company’s profitability. Let’s take a closer look at these factors and understand their importance in evaluating a company’s financial performance.
One of the primary drivers of the EBIT margin is revenue growth. Increasing sales volume and revenue directly contribute to higher EBIT margins, as the company generates more income from its core operations. This can be achieved through various strategies such as expanding into new markets, increasing market share, launching new products, or improving pricing strategies.
It is important to note that revenue growth alone does not guarantee a higher EBIT margin. The company must also manage its costs effectively to ensure that the incremental revenue translates into increased profitability. Therefore, analyzing revenue growth in conjunction with other factors is crucial in evaluating a company’s profitability.
The cost of goods sold (COGS) is another significant factor that affects the EBIT margin. COGS represents the direct costs incurred in producing or acquiring the goods or services that the company sells. These costs include raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overheads.
Managing and controlling COGS is essential for maintaining a healthy EBIT margin. By optimizing the supply chain, negotiating favorable contracts with suppliers, and implementing efficient production processes, a company can reduce its COGS and improve profitability. Additionally, periodic review and adjustment of pricing strategies can help ensure that the company’s products are priced appropriately to cover COGS and generate a profit.
Operating expenses encompass all the costs that a company incurs in its day-to-day operations, excluding COGS. These expenses include salaries and wages, rent, utilities, marketing costs, research and development expenses, and other overhead costs.
Managing operating expenses is crucial in maintaining a healthy EBIT margin. Companies need to strike a balance between investing in growth initiatives and controlling costs. Effective cost management can be achieved through strategies such as streamlining operations, implementing cost-saving measures, and utilizing technology to improve efficiency. By keeping operating expenses in check, a company can improve its EBIT margin and overall profitability.
Depreciation and amortization expenses are non-cash expenses that arise from the gradual wear and tear or the expiration of intangible assets over time. These expenses are deducted from revenue to arrive at EBIT.
While depreciation and amortization expenses do not directly impact a company’s cash flow, they affect the EBIT margin. Higher depreciation and amortization expenses result in lower EBIT margins, as they reduce the company’s operating profit. It is important to consider these expenses when evaluating a company’s profitability, as they can vary significantly depending on the industry and the company’s asset base.
Interest expenses arise from the cost of borrowing funds to finance a company’s operations or investments. As mentioned earlier, interest expenses are not included in the calculation of EBIT, as they can vary significantly from company to company.
However, interest expenses do impact a company’s profitability and overall financial health. Higher interest expenses reduce the company’s net income and can result in lower EBIT margins. Therefore, it is essential to consider the company’s debt levels and interest expenses when assessing its profitability.
Understanding the factors that contribute to the calculation of the EBIT margin is crucial for evaluating a company’s profitability. Revenue growth, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, depreciation and amortization expenses, and interest expenses all play a significant role in determining a company’s EBIT margin and overall financial performance.
By analyzing these factors and their impact on the EBIT margin, investors and analysts can make informed decisions about a company’s financial health and profitability. It is important to consider these factors in conjunction with other financial metrics and industry-specific factors to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s performance.
Ultimately, a higher EBIT margin signifies that a company is generating more profit from its core operations, which is generally seen as a positive indicator of financial health and operational efficiency. By monitoring and evaluating the EBIT margin, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company’s profitability and make informed decisions about investment opportunities or strategic partnerships.
Stay updated with the latest news and exclusive offers. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights delivered to your inbox!